Install SafeSquid Secure Web Gateway using SafeSquid Appliance Builder
Problem
To set up your Secure Web Gateway appliance, you need to first install the Linux operating system on your provisioned hardware. Next, harden the system by implementing best security practices and partition the disks appropriately. Afterward, download and install all necessary dependency libraries and services. Lastly, install, configure, and deploy the Secure Web according to your organization’s environment. Even trials for Secure Web Gateways appliances require complex initial configuration, high technical expertise, and can be extremely time consuming.
SafeSquid Appliance Builder (SAB)
To reduce the complexity, and save time in setting up the Secure Web Gateway, use SafeSquid Appliance Builder (SAB). SAB is a security-enhanced Ubuntu Linux ISO, customized for SafeSquid installation on any physical or virtual hardware within 15 minutes. SAB automatically configures dependent libraries, services, and custom partitioning. On booting from the SAB ISO, Ubuntu is automatically installed, and SafeSquid SWG is downloaded and deployed with all necessary dependency libraries, and services.
Benefits
By automating the manual processes in the installation process, the risk of errors is reduced. Pre-configured settings ensure optimal performance and robust security. Furthermore, SafeSquid Appliance Builder incorporates security best practices in its setup process, providing a hardened system by default.
How to install SafeSquid Secure Web Gateway using SafeSquid Appliance Builder
Prepare the bootable media
Use the latest stable version of SAB to ensure up-to-date features and security patches. Verify the integrity of the downloaded ISO by matching the file’s hash value against the officially disclosed on the website. Remember to back up any important data from the storage media to burn to. Use a reliable tool for burning the ISO to your chosen bootable media, such as Rufus for USB drives or ImgBurn for CDs/DVDs.
Prepare your machine
If the machine’s disk has a different OS installed, backup and format the disk before starting the SafeSquid installation. Then, connect the bootable media to your machine. Restart your computer and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings to set the boot order as
- Primary Boot Device: Hard disk.
- Secondary Boot Device: Bootable Media with SAB
Initial Boot
On booting from the SAB, the SafeSquid installer will guide you through the installation process. Ensure a reliable internet connection as SAB will download updates and SafeSquid software during installation.
Note: If you face any error during installation, press ALT+F4 to get debugging logs. To return to the previous screen press ALT+F1.
Choose Installation Mode
Choose from four installation modes, as per your use cases.
- Standard Installation Mode (Recommended)
Quick and straightforward setup with pre-configured settings. - Expert Installation Mode
Extensive customization and fine-tuning settings - Serial Console Installation (Standard)
Standard Installation on devices with only serial ports - Serial Console Installation (Expert)
Expert Installation on devices with only serial ports
Automate network configuration
Next, the installer will ask for autoconfiguring your network.
To automatically configure network settings via enterprise DHCP service, select Yes.
To manually configure your network settings (for example: to assign a Static IP address), select No.
Set the DNS Search Domain (Only for DHCP)
The DNS Search Domain will be appended to a partially qualified hostname during a DNS lookup. When the gateway requires specific DNS resolution settings that differ from the general network settings provided by DHCP, manually configure the DNS search domain, else keep it empty. Use a relevant search domain to simplify access to internal resources. Ensure the search domain is consistent with the organization's DNS configuration.
Select language
The language selected here will be used for installer and the system.
Select your location
Carefully select the location of the system, as it will be used to set the time zone.
Configure the Keyboard
Keyboard layouts are determined by the country of origin for the keyboard.
Select the appropriate keyboard layout to avoid input issues, especially for non-standard keyboards.
Configure the network
Network interface selection
This will show you the all-network interfaces present in your system. Select the interface that has Internet connectivity as the primary
Assign Static IP address (Skip for DHCP)
Follow any existing IP address allocation policies or guidelines within the organization. Ensure that the IP address falls within the correct subnet range defined by the network and is unique within the network to avoid IP conflicts. For clarity and precision in network configuration, specify the subnet mask and network boundaries by appending the CIDR netmask.
Set Netmask (Skip for DHCP)
Use the appropriate subnet mask that matches the network's addressing scheme.
Specify Gateway (Skip for DHCP)
Enter the correct gateway IP address and verify that the gateway is reachable from the assigned SWG IP address. When the router is your primary device that forwards traffic from your local network to other networks, the router's IP will be your default gateway.
Set Name Server IP (Skip for DHCP)
Use reliable primary and secondary DNS servers for redundancy and ensure DNS servers are correctly configured to resolve domain names properly.
Assign Hostname
Set a meaningful hostname that fits into your network's naming convention. Carefully select the desired hostname, as proper assignment of the Fully Qualified Domain Name would be necessary for integration with other services, like AD.
Assign Domain Name (Skip for DHCP)
Ensure that the domain name is unique and consistent with your organization's naming conventions and existing domain infrastructure. Verify that both forward and reverse DNS entries for the domain name is properly configured in your DNS servers to resolve to the correct IP address.
NTP server Configuration (For Expert Installation)
By default, NTP server has been set to pool.ntp.org. If you have your own NTP server, then you may set to that address for clock synchronization between computer systems to sometime reference.
Choose the mirror of Ubuntu archive
Select the ubuntu archive mirror country geographically closest to the server for fastest download of required packages. Ensure the mirror has good network performance and bandwidth capabilities and is known for known for reliability and minimal downtime.
To adhere to any network policies your organization might have regarding external connections and data downloads, explicitly send the traffic via an HTTP proxy.
Leave this blank if not required and press continue.
Set up users and passwords (For Expert Installation)
Here, you can create the SafeSquid administrator user.
Full Name
Username for your account
Choose password for new user
Ensure that the password created meets the requirements and make sure that you remember this password, as the same will be used to login.
Encrypt your home directory
Choose whether you want to encrypt the user’s home directory
In case of a network-related error, such as "Unable to download debconf preconfiguration," use the installer console to diagnose the root cause and take appropriate action. For further details, please refer to the "Troubleshooting Issues During Installation of SafeSquid" document.
Configure the Clock
Ensure that the detected time zone is correct, the system time zone is crucial for log timestamps, scheduled tasks, and user activities.
Setting Up partitions (If booting via USB Bootable Disk)
Installation will proceed with partitioning process required for SafeSquid automatically.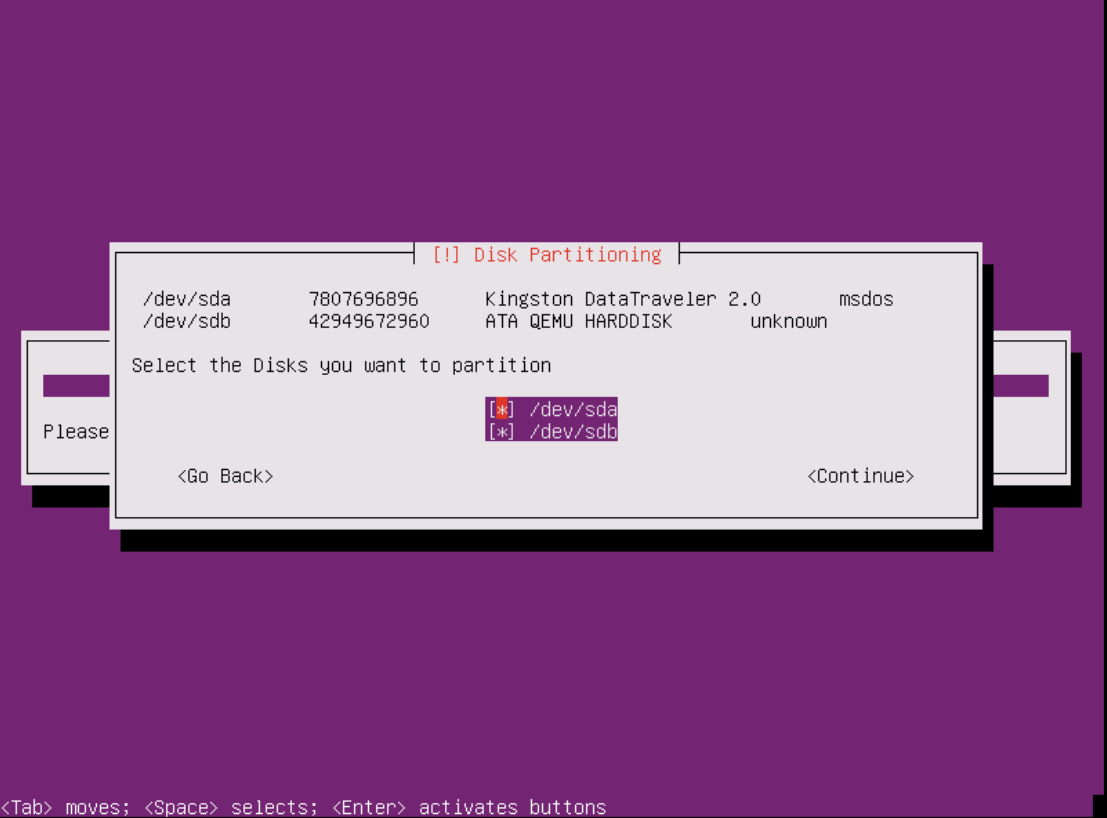
If using a USB as the installation disk, unselect your USB drive from partitioning. For this demonstration /dev/sda is a USB drive which needs to be unselected.
Partition disks (Expert Installation)
You can manually manage partitions.
Writing Partition Changes
Double-check the current partitioning scheme. Make sure it meets your requirements, as no further changes to the partitioning scheme will be possible once LVM is configured. Verify that you are working on the correct disk (in this case, SCSI3 (0,0,0) (sda)). Mistakenly modifying the wrong disk can lead to data loss.
Select yes to manage partitions
Selecting Volume Group Size for Guided Partitioning
When selecting the volume group size for guided partitioning during LVM configuration, it's important to balance current and future needs. You have the option to use the entire volume group for partitioning or just a part of it. Consider reserving some space for future expansions, especially if you plan to add more disks or grow logical volumes later. Ensure the selected size meets the minimum requirements for your operating system and applications, providing sufficient space for immediate needs. Proper partition alignment and minimizing fragmentation can improve performance, while having a backup strategy and reserving space for snapshots can aid in recovery. Regularly monitor disk usage to anticipate future space needs, and specify sizes accurately using supported formats.
Select Method of Partition
Choose from five partition methods, as per your use cases.
- Guided Partitioning
automated disk partitioning with predefined schemes for beginners - Configure Software RAID
Combine multiple physical disks into a single logical unit for redundancy or performance
Supports RAID levels (RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 10) using software. - Configure Local Volume Manager (LVM)
Create resizable and movable logical volumes
Includes setup for physical volumes, volume groups, and logical volumes - Configure Encrypted Volumes
Enables disk encryption to protect sensitive data using technologies like LUKS. - Configure iSCSI Volumes
Configures iSCSI initiators and targets, making remote storage appear as local partitions.
For advanced controls, you can manually select a partition and modify the partition type, size, mount point, and file system.
After configuring the desirable partitioning, select “Finish Partitioning and Write Changes to the Disk” to proceed.
Review Partitioning configuration
Before finalizing the partition changes, thoroughly review the list of partitions and devices being modified to ensure they match your intended setup. Confirm that the partitions to be formatted and their file systems are correct, keeping in mind that this action is irreversible and will erase existing data, so ensure all important data is backed up. Verify that essential system partitions like root and swap are correctly configured and that logical volumes within the volume group are properly set up. Double-check that the correct disk is being modified and that all necessary directories have the right mount points. If there are any uncertainties, use the option to go back and make adjustments before proceeding.
Drive Selection for GRUB (If booting via USB Bootable Disk)
Typically, this drive is the same as the installation disk.
Caution: The GRUB bootloader is essential for booting into the installed system. Installing GRUB on the wrong drive can render the system unbootable.
Note: These additional steps are particularly important for users with specific network configurations or those installed from a USB drive.
Ensure all configurations are double-checked to avoid common installation errors.
Installing Grub
Select No.
It is essential to avoid unmounting /dev/sda, which is your USB bootable device in this case. If /dev/sda is removed, the installation process will be halted, leading to failure.
Select No again
It is essential to avoid unmounting /dev/sda, which is your USB bootable device in this case.
If /dev/sda is removed, the installation process will be halted, leading to failure.
Installation of base system
Finishing installation
The final process of finishing the installation is the last step where the preseed file will be executed.
At the end, the system will reboot itself and goes through some system initialization.
Note: If you have configured your system's boot order with the USB drive or ISO image as the primary boot device, it is likely that the installation menu will reappear upon reboot.
To prevent this, ensure you unmount the USB drive or detach the ISO file from the virtual machine settings before restarting your server.
A welcome screen will appear with SafeSquid (Secure Web Gateway) screen.
Note: If you face any error while installing SafeSquid Appliance
Builder (SAB-ISO), you will get debugging logs information by pressing ALT+F4 to return to previous screen press ALT+F1.
Login to the Server
If you observe the screen by default, it will give you username along with the password.
You need to enter the same username and password for the first login.
Username: administrator
Password: safesquid
You need to reset the password on the first login.
You land into console where SafeSquid SWG will be seen as shown below after successful login.
Post-Installation Checklist and Recommendations
The SafeSquid instance can now be activated from the product interface. To access the product interface, SafeSquid® proxy server must be configured on the web-browser. Post activation, setup SSL Inspection and configure policies as per the enterprise’s requirements.
Related Articles
Standard Installation of SafeSquid using SAB for Baremetal Install with DHCP
When booting from a USB drive ensure the system is set to boot from the USB drive. This might require changing the boot order in BIOS or UEFI settings. Standard Installation The Standard Installation Mode is recommended, and the setup uses mostly ...Standard Installation of SafeSquid using SAB for Baremetal Install with Static IP address
When booting from a USB drive ensure the system is set to boot from the USB drive. This might require changing the boot order in BIOS or UEFI settings. Standard Installation The Standard Installation Mode is recommended, and the setup uses mostly ...Setup Your Secure Web Gateway on your preferred Linux distribution
Overview SafeSquid Appliance Builder (SAB) is an optimized version of Ubuntu Linux, optimized for easy setup of your secure web gateway. The SAB installs the Ubuntu Linux operating system, downloads and deploys the SafeSquid for Linux installation ...Standard Installation of SafeSquid using SAB in a Virtual Machine with DHCP
Standard Installation The Standard Installation Mode is recommended, and the setup uses mostly pre-configured sub-choices. Select Standard install and continue. Network Autoconfigure DHCP Press Yes If you want to use your network DHCP to ...Standard Installation of SafeSquid using SAB in a Virtual Machine with Static IP address
Standard Installation The Standard Installation Mode is recommended, and the setup uses mostly pre-configured sub-choices. Select Standard install and continue. Network Autoconfigure Static Addressing If a static IP is required, select no to manually ...